SpontaneousStratification
Template for model pages.
Project maintained by VicCastillo Hosted on GitHub
SpontaneousStratification
NetLogo Model of Spontaneous Stratification, a natural process in granular mixtures and an example of emergent pattern formation. This model was inspired by a video essay by George W. Hart for the Simons Foundation. See the Reference section for links to videos.
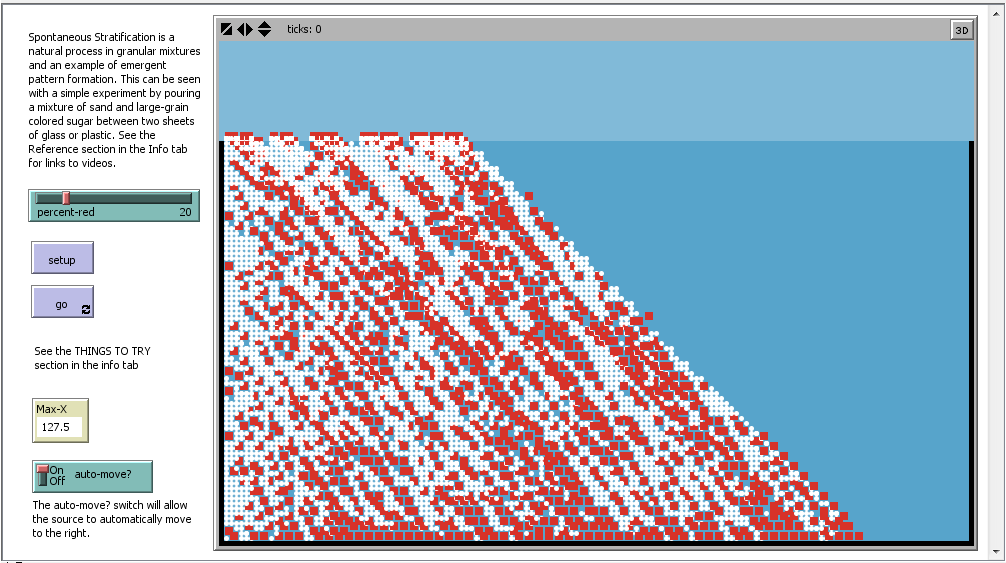
HOW IT WORKS
The white particles are smaller and flow better than the larger red particles. The smaller particles can get trapped by the larger particles while the larger particles flow better in the presence of the smaller particles.
HOW TO USE IT
Adjust the ratio of red particles from zero to one-hundred percent. Press "setup" and then "go". The auto-move? switch will allow the source to automatically move to the right.
THINGS TO NOTICE
Notice the striations (linear patterns) that form automatically.
THINGS TO TRY
With auto-move? set to false, set the percent-red slider to zero (all sand-like particles) and run. What is the Max-X? In other words, how wide is the base? Now, set the percent-red slider to 100 (all sugar-like particles) and run. What is the new base width? What does this say about the two materials?
Now, set the percent-red to 20 (equal volumes because the red particles are four times larger than the white particles). Now run. Do you notice segregation? Why is this happening?
Note that the auto-run? switch allows the top feed to move to the right.
EXTENDING THE MODEL
Add a switch to toggle between spontaneous stratification and spontaneous separation. Hint: consider pure 2D vs. "quasi-2D"
NETLOGO FEATURES
Patch-sets are used to organizing the patches that each turtle tries to occupy, moves from, and moves to. This is especially useful for turtles that need to "occupy" more than one patch. (In NetLogo, a turtle automatically occupies one and only one patch).
CREDITS AND REFERENCES
This is inspired by one of the video essays by George W. Hart for the Simons Foundation
Mathematical Impressions: Spontaneous Stratification by: George Hart May 23, 2014 http://www.simonsfoundation.org/multimedia/mathematical-impressions-multimedia/mathematical-impressions-spontaneous-stratification/
Stratification & Segregation: Spontaneous Stratification & Segregation Schlumberger Excellence in Education Development (SEED) http://www.planetseed.com/relatedarticle/spontaneous-stratification-segregation/
Hernan A. Makse, Shlomo Havlin, Peter R. King, and H. Eugene Stanley. ''Spontaneous Stratification in Granular Mixtures.'' Nature 386 (March 1997): 379:81, http://arxiv.org/pdf/cond-mat/9809432v1/.
Pierre Cizeau, Hernan A. Makse, and H. Eugene Stanley. ''Mechanisms of granular spontaneous stratification and segregation in two-dimensional silos.'' Physical Review E 59 (April 1999).
LICENSE
Spontaneous Stratification Model. CopyRight 2014 Vic Castillo
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 International License.